Researchers worldwide rely on open-source technologies as the foundation of their work. To equip the community with the latest advancements in digital and physical AI, NVIDIA is further expanding its collection of open AI models, datasets and tools — with potential applications in virtually every research field.
At NeurIPS, one of the world’s top AI conferences, NVIDIA is unveiling open physical AI models and tools to support research, including Alpamayo-R1, the world’s first industry-scale open reasoning vision language action (VLA) model for autonomous driving. In digital AI, NVIDIA is releasing new models and datasets for speech and AI safety.
NVIDIA researchers are presenting over 70 papers, talks and workshops at the conference, sharing innovative projects that span AI reasoning, medical research, autonomous vehicle (AV) development and more.
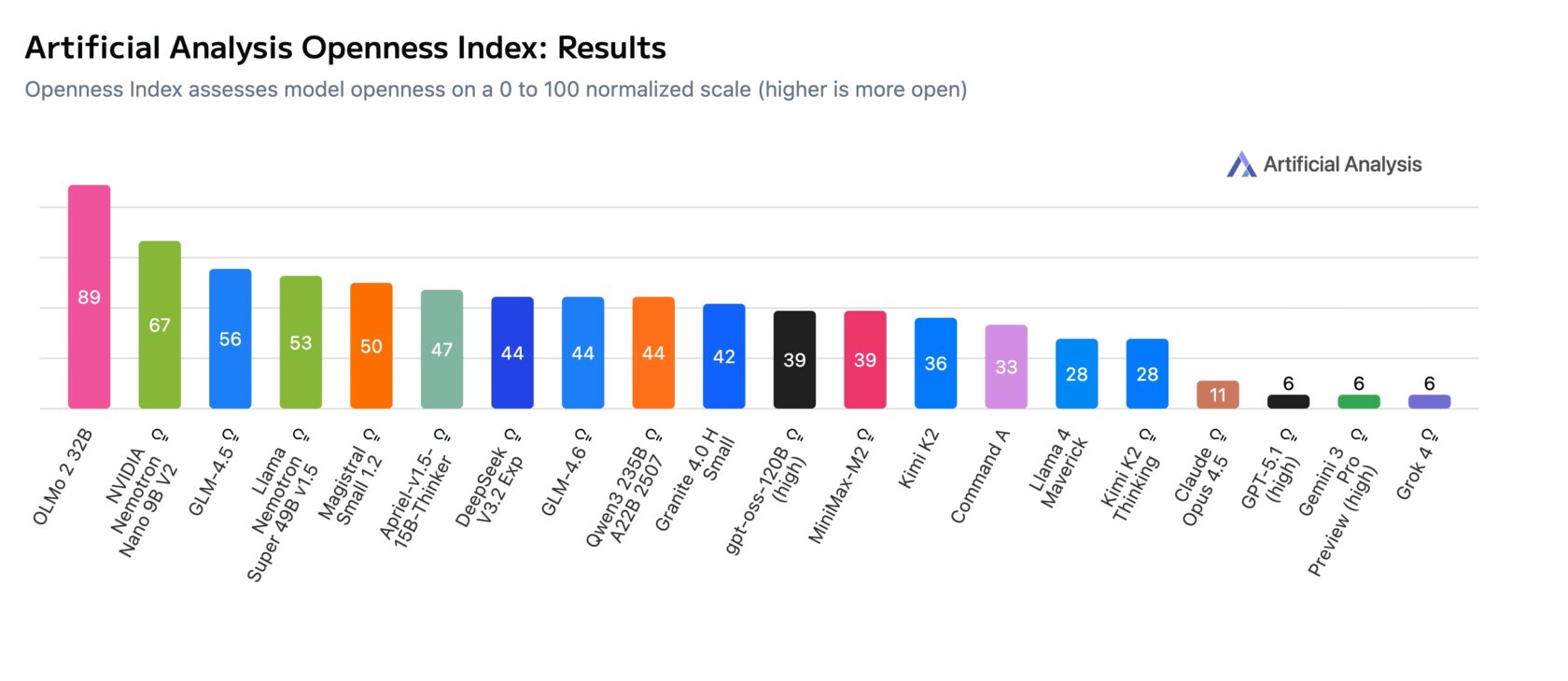
These initiatives deepen NVIDIA’s commitment to open source — an effort recognized by a new Openness Index from Artificial Analysis, an independent organization that benchmarks AI. The Artificial Analysis Open Index rates the NVIDIA Nemotron family of open technologies for frontier AI development among the most open in the AI ecosystem based on the permissibility of the model licenses, data transparency and availability of technical details.
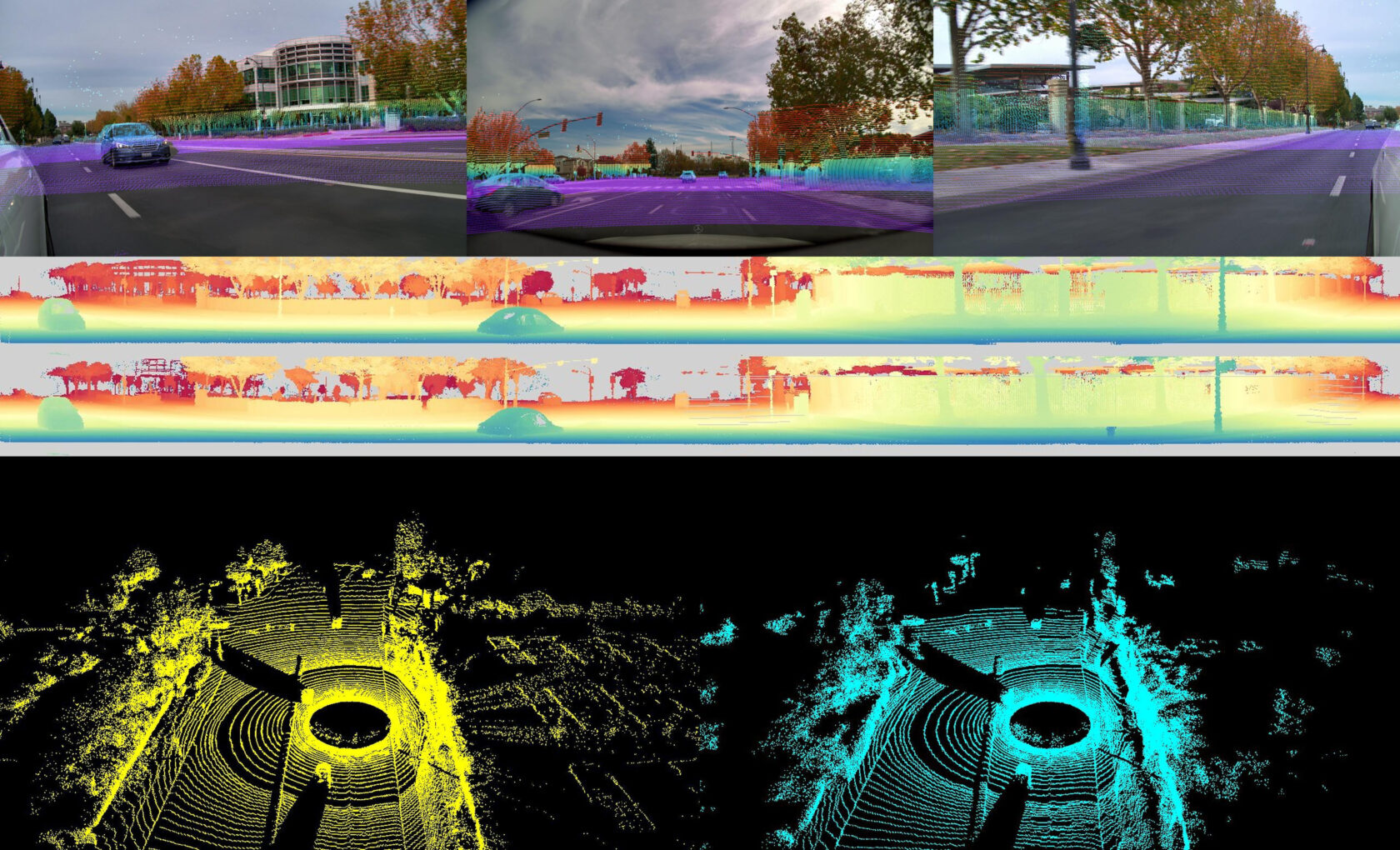
NVIDIA DRIVE Alpamayo-R1 (AR1), the world’s first open reasoning VLA model for AV research, integrates chain-of-thought AI reasoning with path planning — a component critical for advancing AV safety in complex road scenarios and enabling level 4 autonomy.
While previous iterations of self-driving models struggled with nuanced situations — a pedestrian-heavy intersection, an upcoming lane closure or a double-parked vehicle in a bike lane — reasoning gives autonomous vehicles the common sense to drive more like humans do.
AR1 accomplishes this by breaking down a scenario and reasoning through each step. It considers all possible trajectories, then uses contextual data to choose the best route.
For example, by tapping into the chain-of-thought reasoning enabled by AR1, an AV driving in a pedestrian-heavy area next to a bike lane could take in data from its path, incorporate reasoning traces — explanations on why it took certain actions — and use that information to plan its future trajectory, such as moving away from the bike lane or stopping for potential jaywalkers.
AR1’s open foundation, based on NVIDIA Cosmos Reason, lets researchers customize the model for their own non-commercial use cases, whether for benchmarking or building experimental AV applications.
For post-training AR1, reinforcement learning has proven especially effective — researchers observed a significant improvement in reasoning capabilities with AR1 compared with the pretrained model.
NVIDIA DRIVE Alpamayo-R1 will be available on GitHub and Hugging Face, and a subset of the data used to train and evaluate the model is available in the NVIDIA Physical AI Open Datasets. NVIDIA has also released the open-source AlpaSim framework to evaluate AR1.
Learn more about reasoning VLA models for autonomous driving.
Developers can learn how to use and post-train Cosmos-based models using step-by-step recipes, quick-start inference examples and advanced post-training workflows now available in the Cosmos Cookbook. It’s a comprehensive guide for physical AI developers that covers every step in AI development, including data curation, synthetic data generation and model evaluation.
There are virtually limitless possibilities for Cosmos-based applications. The latest examples from NVIDIA include:
Policy models can be trained in NVIDIA Isaac Lab and Isaac Sim , and data generated from the policy models can then be used to post-train NVIDIA GR00T N models for robotics.
NVIDIA ecosystem partners are developing their latest technologies with Cosmos WFMs.
AV developer Voxel51 is contributing model recipes to the Cosmos Cookbook. Physical AI developers 1X, Figure AI, Foretellix, Gatik, Oxa, PlusAI and X-Humanoid are using WFMs for their latest physical AI applications. And researchers at ETH Zurich are presenting a NeurIPS paper that highlights using Cosmos models for realistic and cohesive 3D scene creation.
NVIDIA Nemotron Additions Bolster the Digital AI Developer Toolkit
NVIDIA is also releasing new multi-speaker speech AI models, a new model with reasoning capabilities and datasets for AI safety, as well as open tools to generate high-quality synthetic datasets for reinforcement learning and domain-specific model customization. These tools include:
NVIDIA ecosystem partners using NVIDIA Nemotron and NeMo tools to build secure, specialized agentic AI include CrowdStrike, Palantir and ServiceNow.
NeurIPS attendees can explore these innovations at the Nemotron Summit, taking place today, from 4-8 p.m. PT, with an opening address by Bryan Catanzaro, vice president of applied deep learning research at NVIDIA.
Of the dozens of NVIDIA-authored research papers at NeurIPS, here are a few highlights advancing language models:
View the full list of events at NeurIPS, running through Sunday, Dec. 7, in San Diego.
See notice regarding software product information.